자기 조절 학습(SRL) 측정 방법 비교: 세분성이 중요한 이유
✍️ 이 연구가 다루는 문제는?
자기 조절 학습(Self-Regulated Learning, SRL)은 학생들이 스스로 학습을 계획하고 조절하는 능력입니다. 연구자들은 이를 측정하는 방법으로 자기 보고(Self-Report) 설문지와 행동적 측정(Behavioral Measures) 을 사용합니다. 하지만, 어떤 방법이 더 정확할까? 그리고 측정의 세분성(Granularity) 은 결과에 어떤 영향을 미칠까?
이 논문은 SRL 측정의 정확도를 비교하면서, 세분성이 측정 결과에 어떤 영향을 미치는지를 분석했습니다.
🔍 주요 연구 결과
1️⃣ 자기 보고 설문지는 전반적인 SRL을 측정하는 데는 유용하지만, 세부적인 학습 전략을 측정하는 데는 신뢰성이 낮다.
- 예를 들어, "나는 학습을 잘 계획하는 편이다"와 같은 질문에는 비교적 정확하게 답할 수 있음.
- 하지만 "이 특정 챕터를 공부할 때 요약을 했는가?"라는 질문에는 정확성이 떨어짐.
- 즉, 전반적인 자기 조절 능력을 측정할 때는 유용하지만, 세부적인 학습 전략을 평가할 때는 한계가 있음.
2️⃣ 행동적 측정(Trace Data, Think-Aloud 등)이 세부적인 SRL 전략을 더 정확하게 측정한다.
- 추적 데이터(Trace Data): 온라인 학습에서 학생들의 클릭 패턴, 노트 필기, 복습 여부 등을 기록하는 방식.
- 사고 구술법(Think-Aloud Protocols): 학생이 학습하면서 자신의 생각을 말하도록 유도하는 방식.
- 시선 추적(Eye-Tracking): 학생이 어디를 얼마나 보는지를 측정하는 방식.
- 이러한 방법들은 학생들의 실제 학습 행동을 반영하기 때문에, 특정 학습 전략을 측정하는 데 더 신뢰할 수 있음.
3️⃣ 학업 성취도를 예측하는 데 행동적 측정이 더 효과적이다.
- 행동적 데이터는 학생들의 학습 행동을 직접 반영하기 때문에, 학업 성취도(Academic Achievement)와 더 강한 상관관계를 보임.
- 반면, 자기 보고 설문지는 학생들이 자신의 학습을 과대평가하거나 과소평가할 가능성이 있어 신뢰성이 낮음.
4️⃣ 측정의 세분성이 결과에 큰 영향을 미친다.
- 거친 수준(Coarse-Grained, 전반적인 SRL 측정) → 자기 보고 설문지도 비교적 정확하게 측정 가능.
- 세밀한 수준(Fine-Grained, 특정 학습 전략 측정) → 행동적 측정 방법이 더 적합함.
- 즉, 연구자가 어떤 수준에서 SRL을 측정하려는지에 따라 측정 방법을 신중히 선택해야 함.
5️⃣ 가장 좋은 방법은 다중 방법 접근(Multi-Method Approach)이다.
- 자기 보고 설문지와 행동적 측정을 결합하면 SRL을 더 정확하게 평가할 수 있음.
- 예를 들어, 자기 보고 설문지로 학생들의 전반적인 자기 조절 학습을 측정하고, 행동적 데이터를 활용해 실제 학습 전략을 분석하는 방식이 효과적.
🎯 이 연구가 주는 의미는?
✅ 연구자와 교육자들은 SRL 측정 방법을 신중하게 선택해야 한다.
✅ 자기 보고 설문지는 전반적인 학습 습관을 평가하는 데 유용하지만, 구체적인 학습 전략을 분석하는 데는 한계가 있다.
✅ 학업 성취도를 더 잘 예측하려면 행동적 측정을 활용하는 것이 효과적이다.
✅ SRL을 정확히 측정하기 위해서는 자기 보고와 행동적 측정을 결합하는 다중 방법 접근이 필요하다.
이 연구는 자기 조절 학습 연구와 교육 평가에서 측정 방법을 보다 정교하게 다뤄야 한다는 점을 강조합니다. 학생들이 실제로 어떤 학습 전략을 사용하고 있는지를 객관적인 행동적 데이터와 결합하여 분석하는 것이 앞으로 더 중요해질 것입니다.
💡 한 줄 요약
"자기 조절 학습을 측정할 때는 단순한 설문지만으로는 부족하다. 행동적 데이터를 활용하여 더 정교한 측정 방법을 적용해야 한다!"
Summary in Plain English (5 Sentences)
- This paper examines different ways of measuring self-regulated learning (SRL) and highlights the importance of granularity in determining measurement accuracy.
- The study finds that self-report questionnaires are useful for measuring general SRL abilities, but they are less reliable for tracking specific learning strategies.
- In contrast, behavioral measures like trace data and think-aloud protocols provide more accurate insights into students' actual study behaviors, especially for fine-grained SRL strategies.
- The research also shows that behavioral data is a stronger predictor of academic achievement than self-reports, making it a better tool for educational interventions.
- The paper concludes that a multi-method approach, combining self-reports and behavioral data, is the best way to measure SRL, depending on the research question and level of detail needed.
한국어 번역 (5문장 요약)
- 이 논문은 자기 조절 학습(SRL) 을 측정하는 다양한 방법을 검토하며, 세분성(Granularity) 이 측정 정확성에 중요한 영향을 미친다는 점을 강조한다.
- 연구 결과, 자기 보고 설문지(Self-Report Questionnaires) 는 전반적인 SRL 능력을 평가하는 데 유용하지만, 구체적인 학습 전략을 추적하는 데는 신뢰성이 낮다는 점이 밝혀졌다.
- 반면, 추적 데이터(Trace Data), 사고 구술법(Think-Aloud Protocols) 같은 행동적 측정 방법은 세부적인 SRL 전략을 더 정확하게 파악할 수 있다.
- 또한, 행동적 데이터는 자기 보고보다 학업 성취도를 더 잘 예측할 수 있어, 교육 개입(Intervention)에 더 적합한 측정 방법으로 나타났다.
- 논문은 연구 목적과 필요한 세부 수준에 따라 자기 보고와 행동적 데이터를 결합하는 다중 방법 접근(Multi-Method Approach) 이 SRL을 측정하는 최적의 방식이라고 결론짓는다.
Key Findings of the Research: Granularity Matters in Measuring Self-Regulated Learning (SRL)
This study explored different ways of measuring self-regulated learning (SRL) and examined whether traditional self-report questionnaires provide reliable data compared to behavioral measures such as trace data and think-aloud protocols. The authors found that granularity, or the level of detail at which SRL is measured, plays a crucial role in determining the accuracy of these methods. Below is a breakdown of the key findings.
1. Self-Reports Are Useful for Measuring Global SRL, but Not Specific SRL Strategies
- Global self-regulation (coarse granularity): When SRL is measured at a broad level (e.g., overall learning behaviors or general self-regulation abilities), self-report questionnaires provide a reasonably accurate picture.
- Specific SRL strategies (fine granularity): However, when students are asked about specific learning strategies they used (e.g., highlighting, summarizing, taking notes), self-reports become unreliable. In such cases, behavioral measures (e.g., trace data, eye-tracking, or real-time observations) provide a more accurate account.
Why is Self-Reporting Limited?
- Memory Limitations – Students may not accurately remember the specific strategies they used, leading to errors in self-reports.
- Unconscious Strategies – Some learning behaviors occur without students actively realizing them, making self-reporting difficult.
- Social Desirability Bias – Students might report what they think the researcher wants to hear rather than their actual behavior.
- Generalization Issues – Self-report questionnaires often ask students to describe their general study habits, but these habits can change based on the task or context.
2. Behavioral Measures Provide More Accurate Data on Specific Learning Strategies
- Methods such as trace data (e.g., tracking students' clicks and actions in an online learning system), think-aloud protocols (where students verbalize their thoughts while studying), and eye-tracking (which monitors where students look on a page) capture real-time data.
- These behavioral measures were found to be more accurate in assessing specific SRL strategies than self-reports.
Example Findings from Behavioral Studies
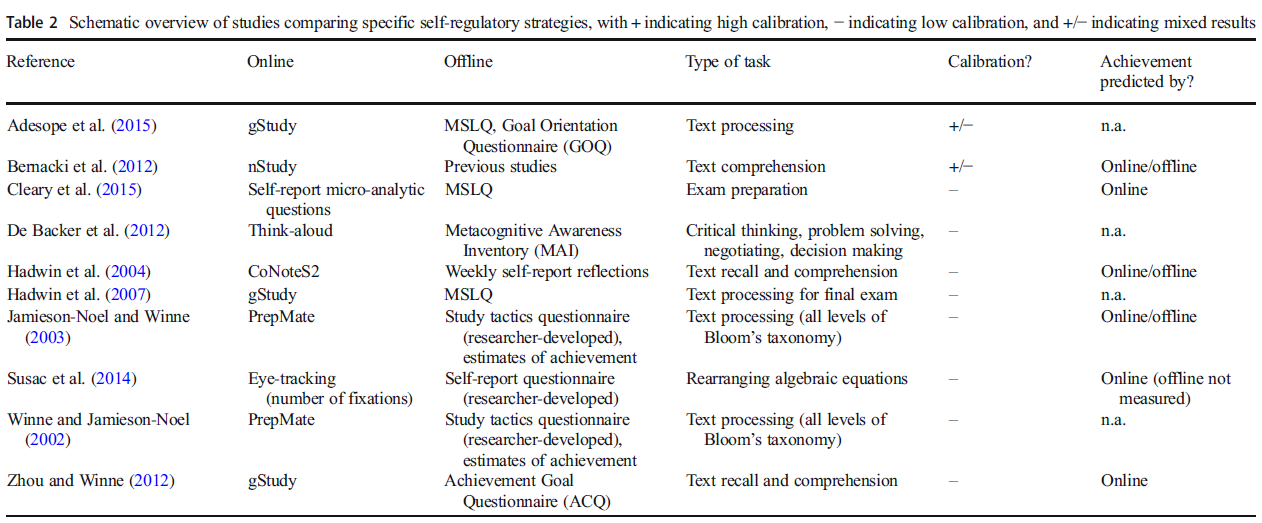
- Winne & Jamieson-Noel (2002) found that students were highly overconfident in reporting their SRL strategies. For example, they claimed to have used study tactics in multiple paragraphs, but trace data showed they did not.
- Hadwin et al. (2007) used the gStudy software to track how students study and found no clear connection between self-reported strategy use and actual behaviors.
- Susac et al. (2014) used eye-tracking and found that students' self-reported strategies did not match their eye movements. Many students thought they were using certain strategies (like checking answers), but their eye movements revealed they were doing something else.
3. Predicting Academic Performance: Which Measure is Better?
- When measuring broad SRL abilities (e.g., how much students regulate their own learning in general), self-reports showed a moderate correlation with students' academic performance.
- When measuring specific strategies, behavioral data (e.g., how often students took notes, highlighted key concepts, or revised their work) had a stronger correlation with academic performance.
Key Comparison
| Measurement Type | Accuracy for Specific SRL Strategies | Accuracy for General SRL | Best for Predicting Performance |
| Self-Report Questionnaires | Low (students overestimate) | High (students can broadly assess their abilities) | Moderate |
| Behavioral Measures (Trace Data, Eye-Tracking, Think-Alouds) | High (tracks real behaviors) | Varies (depends on the method used) | High |
Thus, for educational interventions aimed at improving specific SRL strategies, it is better to use behavioral data rather than self-reports.
4. Combining Multiple Methods Improves SRL Research
- Researchers suggest a multi-method approach, meaning that self-report surveys should not be used alone but should be combined with behavioral measures.
- Why?
- Self-reports provide insight into how students perceive their learning.
- Behavioral measures capture what students actually do.
- Combining the two can give a more complete and accurate picture of SRL.
5. Granularity Explains the Differences in Measurement Accuracy
- Granularity refers to the level of detail at which SRL is measured.
- Coarse-grained SRL (broad self-regulation skills) is well captured by self-reports.
- Fine-grained SRL (specific strategies like summarization, self-testing, or note-taking) is better measured using behavioral data.
Example
- If a researcher asks, "Do you usually plan before studying?", students can accurately self-report this.
- If a researcher asks, "Did you plan before studying this specific chapter?", students might misreport because they do not remember or were unaware of their actions.
This explains why self-reports work well for broad SRL assessments but fail for detailed strategy tracking.
Final Conclusion: Choosing the Right Measurement Based on Research Goals
What to Use When?
- If the goal is to understand general self-regulation trends → Self-report surveys are useful.
- If the goal is to measure specific learning behaviors → Behavioral measures are more accurate.
- If the goal is to predict academic success → A mix of both methods is ideal.
Thus, the study emphasizes that researchers and educators should carefully choose or combine methods depending on their specific research question.
Implications for Education
- Teachers and researchers should not rely solely on self-reports to assess SRL.
- Educational technology (e.g., learning analytics, AI-based tracking tools) should be used more widely to collect accurate behavioral data.
- Students' perceptions of their learning might not always be accurate, so educators should incorporate real-time tracking and interventions to guide them toward better study habits.
Final Thought
This study challenges the long-standing reliance on self-report questionnaires in SRL research and provides strong evidence that behavioral measures offer superior accuracy for detailed SRL analysis. However, it also highlights that self-reports still hold value when measuring SRL at a broad level, making a multi-method approach the best strategy.
By considering granularity, researchers and educators can make better decisions about how to assess and support self-regulated learning in students.
연구의 주요 결과: 자기 조절 학습(SRL) 측정에서 세분성이 중요한 이유
이 연구는 자기 조절 학습(Self-Regulated Learning, SRL) 을 측정하는 다양한 방법을 비교하고, 전통적인 자기 보고(Self-Report) 설문지가 추적 데이터(Trace Data) 나 사고 구술법(Think-Aloud Protocols) 같은 행동적 측정 방법과 비교했을 때 신뢰할 수 있는 데이터를 제공하는지 여부를 분석했습니다. 연구 결과, 세분성(Granularity) 즉, SRL을 얼마나 세밀한 수준에서 측정하는지가 측정 방법의 정확성을 결정하는 중요한 요소임을 발견했습니다. 다음은 주요 연구 결과를 요약한 내용입니다.
1. 자기 보고(Self-Report)는 전반적인 SRL을 측정하는 데는 유용하지만, 세부적인 SRL 전략 측정에는 부정확하다
- 전반적인 자기 조절 능력(Coarse Granularity): 학습자들이 전반적으로 자기 조절 학습을 얼마나 잘하는지 평가할 때는 자기 보고 설문지가 비교적 신뢰할 수 있습니다.
- 구체적인 SRL 전략(Fine Granularity): 그러나 특정한 학습 전략(예: 밑줄 긋기, 요약하기, 노트 정리하기)을 얼마나 자주 사용했는지 물어볼 경우, 자기 보고 방식은 부정확한 결과를 초래했습니다. 이러한 경우 추적 데이터(Trace Data), 사고 구술법(Think-Aloud Protocols), 혹은 시선 추적(Eye-Tracking) 같은 행동적 측정 방법이 더 신뢰할 수 있는 결과를 제공했습니다.
자기 보고 방식이 한계를 가지는 이유
- 기억 오류(Memory Limitations) – 학생들은 특정 학습 전략을 사용한 경험을 정확하게 기억하지 못할 수 있습니다.
- 무의식적 전략(Unconscious Strategies) – 학습 과정에서 일부 전략은 자동적으로 이루어질 수도 있기 때문에, 학생들이 자신이 사용한 전략을 인식하지 못할 수 있습니다.
- 사회적 바람직성 편향(Social Desirability Bias) – 학생들은 실제로 사용한 전략이 아니라 연구자가 기대하는 답변을 할 가능성이 있습니다.
- 일반화 문제(Generalization Issues) – 자기 보고 설문지는 특정한 학습 상황이 아니라 일반적인 학습 습관을 평가하는 경우가 많아, 특정한 과제나 상황에서 어떤 전략을 사용했는지를 정확하게 반영하지 못할 수 있습니다.
2. 행동적 측정 방법(Trace Data, 사고 구술법 등)은 구체적인 학습 전략을 측정하는 데 더 정확하다
- 추적 데이터(Trace Data): 온라인 학습 환경에서 학생들이 클릭한 항목, 메모한 내용, 학습 자료를 본 시간을 기록하는 방식.
- 사고 구술법(Think-Aloud Protocols): 학생들이 학습 중에 자신이 생각하는 과정을 소리 내어 말하도록 유도하는 방식.
- 시선 추적(Eye-Tracking): 학생들이 특정 학습 자료를 볼 때 어디에 집중하는지를 측정하는 방식.
행동적 측정 방법과 자기 보고 설문지의 비교 연구 사례
- Winne & Jamieson-Noel (2002) 연구에서는 학생들이 특정한 학습 전략을 사용했다고 과대평가(overestimate) 하는 경향이 있음을 발견했습니다. 예를 들어, 학생들은 여러 문단에서 학습 전략을 사용했다고 보고했지만, 추적 데이터 분석 결과 실제로는 사용하지 않았음이 드러났습니다.
- Hadwin et al. (2007) 연구에서는 gStudy 소프트웨어를 사용하여 학생들의 학습 행동을 분석한 결과, 자기 보고된 전략 사용과 실제 행동 사이에 거의 일관성이 없음을 확인했습니다.
- Susac et al. (2014) 연구에서는 시선 추적(Eye-Tracking) 기술을 사용해 학생들이 특정 문제를 해결하는 동안 어디를 보는지를 측정했는데, 학생들이 자기 보고 설문지에서 응답한 내용과 실제 눈의 움직임이 다르다는 것이 밝혀졌습니다. 즉, 학생들이 스스로 어떤 학습 전략을 사용했는지 정확히 인식하지 못하는 경우가 많음을 보여주었습니다.
3. 학업 성취도를 예측하는 데 어떤 측정 방법이 더 효과적인가?
- 전반적인 자기 조절 능력(Global SRL) 을 측정할 때는 자기 보고 설문지가 학업 성취도와 어느 정도 관련이 있음을 보였습니다.
- 구체적인 학습 전략(Specific Strategies) 을 측정할 때는 행동적 데이터(예: 학습 중 노트 필기, 요약, 자기 점검)가 학업 성취도를 예측하는 데 더 강력한 상관관계를 가짐이 확인되었습니다.
핵심 비교
| 측정 방법 | 특정 SRL 전략 측정 정확도 | 전반적인 SRL 측정 정확도 | 학업 성취도 예측 |
| 자기 보고 설문지(Self-Report Questionnaires) | 낮음 (학생들이 과대평가) | 높음 (전반적인 경향은 파악 가능) | 보통 |
| 행동적 측정(Trace Data, 사고 구술법 등) | 높음 (실제 행동을 측정) | 상황에 따라 다름 | 높음 |
따라서 구체적인 SRL 전략을 개선하기 위한 교육적 개입(Intervention)이 필요하다면, 행동적 데이터를 활용하는 것이 더 효과적입니다.
4. 다중 방법 접근(Multi-Method Approach)이 가장 효과적인 SRL 측정 방법이다
- 연구자들은 하나의 측정 방법만 사용하는 것이 아니라, 여러 방법을 결합하는 것이 가장 정확한 결과를 제공한다고 주장합니다.
- 왜?
- 자기 보고 설문지는 학생들이 자신의 학습을 어떻게 인식하는지에 대한 통찰을 제공합니다.
- 행동적 측정 방법은 학생들이 실제로 어떻게 학습하는지를 보여줍니다.
- 두 가지 방법을 결합하면 SRL에 대한 보다 완전한 이해가 가능합니다.
5. 세분성(Granularity)이 측정 정확성을 결정하는 핵심 요소다
- 세분성(Granularity) 이란 SRL을 얼마나 구체적인 수준에서 측정하는지를 의미합니다.
- 거칠게 측정(Coarse Granularity, 전반적인 SRL) → 자기 보고 방식이 비교적 정확함.
- 세밀하게 측정(Fine Granularity, 특정한 SRL 전략) → 행동적 측정 방법이 더 정확함.
예시
- 연구자가 "당신은 보통 학습을 계획합니까?" 라고 묻는다면, 학생들은 비교적 정확하게 응답할 수 있습니다.
- 하지만 "당신은 이 특정한 챕터를 공부하기 전에 계획을 세웠습니까?" 라고 묻는다면, 학생들은 정확히 기억하지 못할 가능성이 높아 자기 보고의 신뢰성이 떨어집니다.
따라서 연구자가 SRL을 측정할 때, 연구 목표에 따라 적절한 세분성을 설정하는 것이 중요합니다.
최종 결론: 연구 목표에 따라 적절한 측정 방법을 선택해야 한다
측정 방법 선택 가이드
- 전반적인 자기 조절 학습 경향을 파악하려면 → 자기 보고 설문지가 유용하다.
- 구체적인 학습 전략을 측정하려면 → 행동적 측정 방법이 더 정확하다.
- 학업 성취도를 예측하려면 → 두 가지 방법을 함께 사용하는 것이 이상적이다.
결론적으로, 연구자들과 교육자들은 연구 목표에 따라 측정 방법을 신중하게 선택하거나 결합해야 하며, 자기 보고 설문지만으로는 SRL을 완전히 측정할 수 없다는 점을 이해해야 합니다.
이 연구는 자기 보고 방식에 대한 맹목적인 신뢰를 재고하고, 행동적 측정 방법을 더 적극적으로 활용할 필요성을 강조하고 있습니다.
다음은 논문의 논의(Discussion) 부분에서 핵심적인 메시지를 전달하는 다섯에서 열 개의 문장을 번역한 것입니다.
- "Granularity was found to be an important construct when it comes to the comparison between offline self-reports and online measurements, influencing the level of convergence between students’ self-reports and behavioral indicators of SRL."
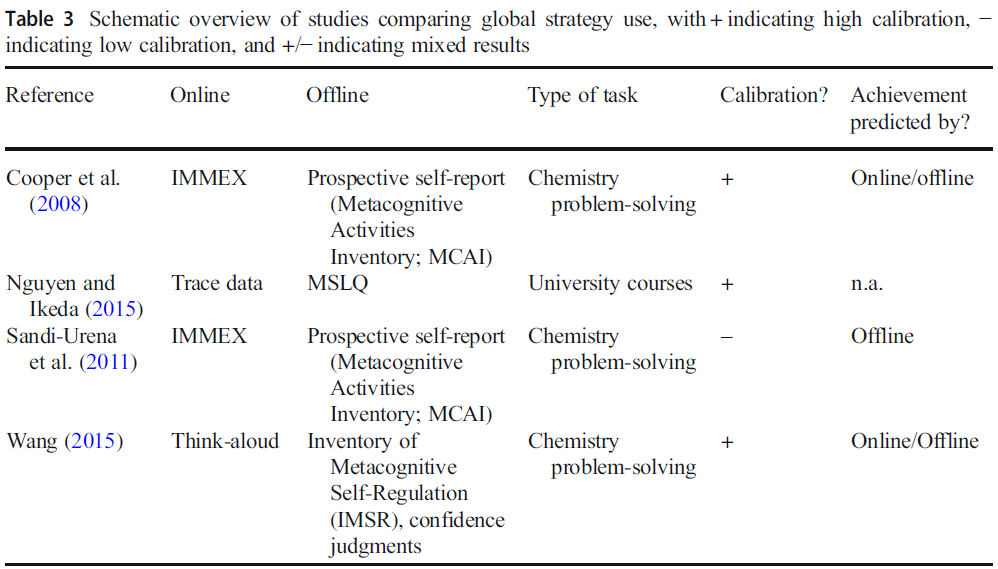
→ 세분성(Granularity)은 오프라인 자기 보고(Self-Report)와 온라인 측정(Online Measurement)을 비교할 때 중요한 개념으로, 학생들의 자기 보고와 행동적 지표 간의 일치도(Convergence)에 영향을 미치는 요소임이 밝혀졌다. - "Studies that indicate high calibration are mainly those with a focus on students’ global use of self-regulatory strategies (coarse grained)."
→ 높은 보정력(Calibration)이 나타난 연구들은 주로 학생들의 전반적인 자기 조절 학습 전략 사용(거친 수준, Coarse-Grained)에 초점을 맞춘 경우였다. - "Studies that focus on calibration of concrete self-regulatory strategies (fine grained) generally indicate a low degree of calibration."
→ 구체적인 자기 조절 학습 전략(세밀한 수준, Fine-Grained)의 보정을 연구한 경우, 일반적으로 낮은 수준의 보정력이 관찰되었다. - "If a link should be made to learning outcomes, trace data have been found to be a more powerful predictor."
→ 학습 성과(Learning Outcomes)와의 연관성을 분석할 때, 추적 데이터(Trace Data)가 더 강력한 예측 변수(Predictor)로 작용하는 것으로 나타났다. - "Self-report questionnaires have their own value in educational research and remediation, in the sense that they might give a relatively accurate insight into students’ global level of metacognition, serving as a starting point for more precise interventions."
→ 자기 보고 설문지는 교육 연구와 개선(Remediation)에서 나름의 가치를 가지며, 학생들의 전반적인 메타인지 수준을 비교적 정확하게 파악할 수 있는 수단이 될 수 있다. 또한, 보다 정밀한 개입(Intervention)의 출발점으로 활용될 수 있다. - "Researchers and educationalists think carefully about the research questions or problems they wish to address, being aware of the affordances and limitations of different measurement methods, and align their measurements to the issues at hand."
→ 연구자들과 교육자들은 자신이 해결하고자 하는 연구 질문이나 문제를 신중하게 고려해야 하며, 각 측정 방법의 장점과 한계를 인식하고 연구 목표에 맞는 측정 방식을 선택해야 한다. - "When using online measures of SRL, the operationalization of strategies is an important consideration."
→ 온라인 방식으로 자기 조절 학습(SRL)을 측정할 때는, 전략을 어떻게 조작적으로 정의하고 측정할 것인지가 중요한 고려 사항이다. - "The distinction between measurement of global SRL versus specific strategies could also explain why the behavioral measures of SRL tend to be better predictors of academic achievement than students’ self-reports."
→ 전반적인 자기 조절 학습과 구체적인 학습 전략을 측정하는 방식의 차이가, 행동적 측정 방법이 자기 보고보다 학업 성취도를 더 잘 예측하는 이유를 설명할 수 있다. - "Future research should focus on clearly delineating the predictive effect of individual strategies on specific learning tasks in higher education, in order to further inform interventions to enhance SRL in students."
→ 향후 연구에서는 개별 학습 전략이 특정 학습 과제에서 미치는 예측 효과를 명확히 규명하여, 학생들의 자기 조절 학습을 향상시키기 위한 개입 방안을 보다 정교하게 개발해야 한다. - "A firm theoretical grounding is important—measures of SRL should be closely aligned to their underlying models, which in the reported studies is often not the case."
→ 강력한 이론적 기반이 중요하며, 자기 조절 학습(SRL)의 측정 방식은 그 기저 모델과 밀접하게 연계되어야 한다. 하지만, 기존 연구에서는 이러한 연계가 충분하지 않은 경우가 많았다.
이 문장들은 논문의 핵심 결론을 강조하며, 세분성이 측정 방법의 정확성에 미치는 영향, 자기 보고 설문지의 한계, 행동적 측정 방법의 강점, 연구 설계에서 고려해야 할 사항 등을 명확하게 설명하고 있습니다.
Rovers, S. F., Clarebout, G., Savelberg, H. H., De Bruin, A. B., & van Merriënboer, J. J. (2019). Granularity matters: comparing different ways of measuring self-regulated learning. Metacognition and Learning, 14, 1-19.
'논문 읽기 (with ChatGPT)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 빠른 사고와 느린 사고를 넘어서: 변이이론적 임상추론 및 오류 모델이 교육, 평가, 그리고 연구에 미치는 영향 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
|---|---|
| 정보기반 근거이론 (Informed Grounded Theory) (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 존재, 성장, 그리고 소속감: 의학에서의 전문직 정체성 형성의 재개념화 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 근거기반실무 교육 개입의 보고 완전성: 체계적 검토 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 소아 응급실에서의 레지던트 민감 품질 지표: 감독자 신뢰도 및 환자 중증도·복잡성과의 관계 탐색 (0) | 2025.02.24 |