
👩⚕️ 존재, 성장, 그리고 소속감: 의사가 되어가는 과정 속에서 나를 찾기
의사가 된다는 것은 단순히 의학 지식을 배우고, 기술을 익히는 것만이 아닙니다. **"나는 어떤 의사로 살아갈 것인가?"**라는 질문에 대한 답을 찾아가는 과정이기도 합니다. 이 논문에서는 기존의 전문직 정체성 형성 모델이 가진 문제점을 짚어보고, 더 나은 방향을 제시하고 있습니다. 함께 살펴볼까요? 👀
📌 기존의 전문직 정체성 형성: 한 가지 길만 있는 걸까?
의학 교육에서는 전문직 정체성을 형성하는 과정이 중요하게 여겨집니다. 기존 모델에서는 **"사회화(socialization)"**를 통해 의사라는 직업의 가치와 규범을 익히고, 이를 내면화하는 것이 핵심이라고 보았는데요.
하지만 이런 접근에는 문제가 있습니다. ❌
✔️ 모두가 같은 방식으로 성장해야 한다는 암묵적인 강요
✔️ 소수자(여성, 인종적 소수 그룹, LGBTQ+)가 소외될 가능성
✔️ 지배적인 문화(백인, 남성 중심)에 맞춰야 한다는 부담
결국, 기존 모델은 다양한 배경을 가진 학습자들에게 적합하지 않을 수 있으며, 일부는 자신의 정체성을 억누르면서까지 동화(conformity)해야 한다는 압박을 받을 수도 있습니다.
🔄 새로운 관점: 존재(Being), 성장(Becoming), 그리고 소속감(Belonging)
이 논문에서는 전문직 정체성 형성을 더 유연하고, 포용적인 관점에서 바라봅니다. 핵심 키워드는 바로 **"존재, 성장, 그리고 소속감"**입니다.
✅ 1. 존재 (Being) – 의과대학에 들어올 때 이미 개인적인 정체성을 가지고 있습니다. 우리는 각자 다른 경험과 배경을 가진 존재이며, 이것이 의사로 성장하는 데 중요한 요소입니다.
✅ 2. 성장 (Becoming) – 의사로서 정체성은 고정된 것이 아니라 계속 변화하고 발전하는 것입니다. 한 가지 길만 있는 것이 아니라, 각자의 방식으로 성장할 수 있어야 합니다.
✅ 3. 소속감 (Belonging) – 단순히 기술을 익히는 것이 아니라, 의료 공동체에서의 소속감이 중요합니다. 소외감 없이 진정한 나로서 의사로 성장할 수 있어야 합니다.
이 모델은 기존의 사회화 개념을 수동적인 내면화가 아닌, 적극적인 비판과 참여의 과정으로 보고 있습니다. 👏
👥 의사 정체성 형성에 영향을 미치는 요소들
그렇다면 의사로서의 정체성 형성에는 어떤 요소들이 영향을 미칠까요? 🤔
💡 사회적 환경: 시대에 따라 의사의 역할과 기대가 변합니다. 예를 들어, 팬데믹 이후 의료진의 역할이 더욱 강조되었죠.
👩🏫 멘토와 롤모델: 좋은 멘토는 긍정적인 영향을 미치지만, 만약 적절한 롤모델이 없다면 학습자는 소속감을 느끼지 못할 수도 있습니다.
📱 소셜 미디어와 가상 공동체: 요즘은 온라인에서 전문직 네트워크를 형성하는 경우도 많아졌습니다. 하지만 개인과 직업적 정체성이 뒤섞이는 문제도 생길 수 있습니다.
🏥 교육 시스템과 문화: 각 학교와 병원의 문화에 따라 전문직 정체성 형성 방식도 다릅니다.
이처럼 다양한 요소들이 복합적으로 작용하며, 의사 개개인의 정체성 형성에 영향을 미칩니다.
💡 우리가 나아가야 할 방향
결국, 중요한 것은 "나는 어떤 의사가 되고 싶은가?" 하는 질문입니다. 의사는 단순히 의료 기술을 가진 사람이 아니라, 자신만의 가치와 신념을 가진 전문가입니다.
💙 모든 학습자가 자신의 정체성을 유지하면서도 성장할 수 있는 환경이 필요합니다.
💙 사회화 과정이 동화(conformity)가 아니라, 비판적 사고와 자기 주도적인 참여를 포함해야 합니다.
💙 다양한 배경과 관점을 가진 사람들이 함께 성장할 수 있도록 교육 시스템이 변화해야 합니다.
이 논문은 전문직 정체성 형성에 대한 새로운 관점을 제시하며, 더 포용적이고 유연한 방식으로 의료 교육이 발전해야 함을 강조합니다.
🎯 마무리하며…
의사가 된다는 것은 긴 여정입니다. 🎢 그리고 그 과정에서 우리는 계속 변하고 성장합니다. 이 논문이 말하는 것처럼, 의사가 되는 과정은 정해진 길이 있는 것이 아니라, 각자 자기만의 방식으로 존재하고, 성장하며, 소속감을 찾는 과정이어야 합니다.
여러분은 어떤 의사가 되고 싶으신가요? 😊💬
Summary in Plain English (Five Sentences)
- This paper argues that professional identity formation (PIF) in medicine should be seen as an active process where learners critically engage with professional norms, rather than simply adopting them.
- Traditional PIF models have unintentionally excluded underrepresented groups by reinforcing dominant cultural norms and expecting conformity.
- The authors propose a revised framework that emphasizes learner agency, the evolving nature of identity, and the importance of belonging in medical communities.
- Factors like socialization, mentorship, role models, and external societal influences shape how medical trainees develop their professional identity.
- The ultimate goal is to train physicians who are not only competent but also authentic, inclusive, and capable of meeting the diverse needs of society.
한국어 요약 (다섯 문장)
- 이 논문은 의학에서의 전문직 정체성 형성이 단순한 규범 내면화가 아니라, 학습자가 적극적으로 비판적으로 참여하는 과정이어야 한다고 주장한다.
- 기존의 전문직 정체성 형성 모델은 지배적인 문화 규범을 강화하면서, 소외된 집단을 무의식적으로 배제하는 문제를 가지고 있었다.
- 저자들은 학습자의 주체성, 정체성의 변화 가능성, 그리고 의료 공동체에서의 소속감의 중요성을 강조하는 새로운 틀을 제안한다.
- 사회화 과정, 멘토링, 롤모델, 그리고 외부 사회적 요인 등이 의료 교육생의 전문직 정체성 형성에 영향을 미친다.
- 궁극적인 목표는 유능할 뿐만 아니라 진정성 있고 포용적인 태도를 가지며, 다양한 사회적 요구를 충족할 수 있는 의사를 양성하는 것이다.
이 논문의 핵심 문장 (Punchline Sentences) 및 선정 이유
1.
"The process of socialization was, and continues to be, foundational in forming a professional identity. However, the working definition of socialization that predominates in the literature, 'the process by which a person learns to function within a particular society or group by internalizing its values and norms,' now appears insufficient."
✅ 선정 이유:
기존의 사회화(socialization) 개념이 단순한 가치와 규범의 내면화가 아니라, 보다 적극적인 비판적 관여가 필요함을 강조하는 핵심 문장이다. 기존 개념의 한계를 명확히 지적하면서, 논문이 제안하는 새로운 패러다임의 필요성을 제시하는 역할을 한다.
2.
"Evolutions in the understandings of professional identity formation, as described in this paper, include re-defining socialization as an active process involving critical engagement with professional norms, emphasizing the role of agency, and recognizing the importance of belonging or exclusion on one’s sense of professional self."
✅ 선정 이유:
논문이 제안하는 전문직 정체성 형성의 새로운 접근법을 간결하게 요약하는 문장이다. 사회화를 수동적 과정이 아닌 적극적 과정으로 바라보고, 학습자의 주체성(agency)과 소속감(belonging)의 중요성을 강조하는 핵심 개념을 포함하고 있다.
3.
"There is also evidence that many learners from social groups under-represented in medicine experience identity threat and exclusion."
✅ 선정 이유:
기존의 전문직 정체성 형성 모델이 소수자들에게 불평등하게 작용할 가능성이 있음을 명확하게 지적하는 문장이다. 특히, 기존 체계가 특정 사회 집단에게 불리하게 작용할 수 있다는 점을 강조하면서, 교육 개혁의 필요성을 설득력 있게 제시한다.
4.
"Given that professional identities are social constructs, their nature has evolved alongside changes in societal norms and expectations."
✅ 선정 이유:
전문직 정체성이 고정된 것이 아니라 사회적·문화적 변화에 따라 진화하는 개념임을 강조하는 문장이다. 의학교육이 이러한 변화에 적응하고 반영해야 함을 시사하며, 논문의 핵심 주장과 연결된다.
5.
"For educators, this highlights the importance of assisting learners in reflecting on, and being explicit about how their identities and backgrounds shape who they wish to be and become."
✅ 선정 이유:
의학교육자들의 역할을 명확히 정의하는 문장이다. 단순히 지식을 전달하는 것이 아니라, 학습자가 자신의 정체성을 성찰하고 성장할 수 있도록 도와주는 역할이 필요하다는 점을 강조한다.
6.
"Socialization should not force learners to suppress aspects of their identity to conform to dominant norms."
✅ 선정 이유:
사회화 과정이 학습자에게 불필요한 동화(conformity) 압력을 주어서는 안 되며, 개인의 정체성을 억압하지 않는 방식으로 진행되어야 한다는 중요한 메시지를 담고 있다. 이는 정체성 형성 과정에서 포용성과 다양성을 유지해야 한다는 논문의 핵심 주장과 연결된다.
7.
"The explicit emphasis on belonging highlights the need for educators to attend not just to full participation in medical acts but also to meaningful inclusion into communities of practice through valuing and recognizing the individuality and diverse perspectives of their learners."
✅ 선정 이유:
단순한 기술 습득을 넘어 의료 공동체에서의 의미 있는 포용과 소속감이 필수적임을 강조하는 문장이다. 학습자의 개별성과 다양한 관점을 존중하는 것이 교육자들에게 중요한 과제임을 시사한다.
8.
"Authentic practice is directly linked to health outcomes, which alone provides a justification for review and change."
✅ 선정 이유:
전문직 정체성 형성이 단순한 교육적 개념이 아니라, 실제 환자의 건강 결과(health outcomes)와 직결되는 중요한 문제임을 강조하는 문장이다. 이를 통해, 논문이 제안하는 변화가 단순한 이론적 논의가 아니라 실제 의료의 질 개선과 연결되어야 함을 강하게 주장한다.
9.
"It is therefore almost certain that further updates will be needed as we continue to learn and grow as physicians, people, and societies."
✅ 선정 이유:
의학 교육과 전문직 정체성 형성은 고정된 개념이 아니라 지속적으로 발전해야 하는 개념임을 강조하는 문장이다. 사회적 변화와 의료 환경의 변화를 반영하여 지속적인 개선이 필요함을 명확히 전달한다.
10.
"The goal is to prepare future physicians who are competent, compassionate, and equipped to meet the diverse needs of society."
✅ 선정 이유:
논문의 궁극적인 목표를 명확하게 요약하는 문장이다. 단순히 기술적으로 유능한 의사를 양성하는 것이 아니라, 공감력을 갖추고 사회의 다양한 요구를 충족할 수 있는 의사를 양성하는 것이 핵심 목표임을 강조한다.
총평
이 논문은 기존의 전문직 정체성 형성 모델이 갖는 한계를 비판하고, 더 포괄적이고 역동적인 모델을 제안하는 것을 목표로 한다. 위에서 선정한 문장들은 논문의 핵심 개념(사회화의 재개념화, 소속감의 중요성, 교육자의 역할, 지속적인 변화 필요성 등)을 가장 효과적으로 전달하며, 논문의 논지를 강력하게 뒷받침하는 내용들이다. 🚀
Thorough Explanation of Each Section of the Article
Title: Being, Becoming, and Belonging: Reconceptualizing Professional Identity Formation in Medicine
Introduction
Over the last decade, there has been a shift in medical education from focusing on professionalism (i.e., professional behaviors and competencies) to the broader concept of professional identity formation (PIF)—how medical trainees develop their sense of self as physicians. This shift has been largely positive but has also revealed unintended harmful consequences.
- Identity Threat & Exclusion: Traditional models of PIF often fail to recognize the experiences of marginalized groups, leading to exclusion or pressure to conform to dominant norms.
- Overemphasis on Dominant Cultural Norms: The profession has historically been shaped by the values of dominant cultural groups (e.g., white, male, straight), potentially alienating those who do not fit this mold.
The authors propose a reconceptualization of professional identity formation that:
- Treats socialization as an active process where learners critically engage with professional norms.
- Emphasizes learner agency, allowing them to shape their professional identities.
- Recognizes the importance of belonging and the risks of exclusion.
The goal is to create a more inclusive framework for identity formation in medicine, while still ensuring high professional standards.
The Process of Professional Identity Formation
This section outlines how professional identity is formed through socialization into medicine. The authors argue that previous models did not fully account for power dynamics and the ways in which professional identity formation often requires assimilation into dominant cultural norms.
Pre-existing Personal and Professional Identities at Entry into the Program
- Medical students enter training with pre-existing identities shaped by their personal experiences, social background, and prior education.
- These identities influence how they engage with the profession and how they experience socialization.
- Identities are not static but evolve over time as learners interact with the medical community.
Key takeaway: Medical trainees are not blank slates—their identity development begins before medical school.
Socialization and Learner Responses
- Socialization is traditionally defined as the process of adopting the values and norms of a group. However, this definition implies passive internalization rather than active engagement.
- The authors emphasize that learners do not just absorb norms—they can:
- Accept professional values.
- Resist or critique them.
- Negotiate their place within the profession.
- Socialization should not force learners to suppress aspects of their identity to conform to dominant norms.
Key takeaway: Professional identity formation is not just about fitting in—it should allow for critical engagement and diversity.
Evolving Personal and Professional Identities
- Professional identity is not fixed but continues evolving throughout one’s career.
- As learners progress through medical training (e.g., medical student → resident → attending), they develop new identities that reflect their growing experience.
- However, professional identity is often seen as separate from personal identity, leading some trainees to feel inauthentic—they may adopt a professional "persona" that does not fully align with their personal self.
Key takeaway: Authenticity is crucial—learners should be supported in integrating personal and professional identities.
Communities of Practice
- Medical trainees engage in multiple communities of practice (e.g., medical school, residency programs, hospital teams, professional organizations).
- Belonging to these communities shapes identity, but not everyone feels equally included.
- The term “Communities of Practice” is used instead of a singular "Community of Practice" to reflect the diversity of professional environments trainees interact with.
Key takeaway: Medical identity is shaped by multiple overlapping professional communities, and inclusion matters.
Summary of the Process of Professional Identity Formation
This section summarizes the revised framework for professional identity formation:
- Identity formation is a social process influenced by diverse factors.
- Learners enter medicine with unique pre-existing identities.
- Socialization is an active, critical process, not passive assimilation.
- Professional and personal identities co-evolve over time.
- A sense of belonging is crucial to professional development.
The new model encourages educators to support diversity and foster authenticity rather than imposing a single professional identity.
Factors Influencing the Socialization Process
Professional identity formation is not isolated from the real world. Several factors shape how trainees experience socialization:
- The Sociopolitical Context:
- Events like the Black Lives Matter movement and #MeToo have raised awareness of discrimination in medicine.
- Medical schools must address issues of equity, diversity, and inclusion in their curricula.
- The Hidden Curriculum:
- Unspoken norms, values, and attitudes in medical education shape professional identity just as much as formal coursework.
- Role Models & Mentorship:
- Learners need diverse role models who reflect different identities and perspectives.
- The lack of mentors from underrepresented groups can reinforce feelings of exclusion.
- Social Media & Virtual Communities:
- Online communities allow for professional networking but also blur personal and professional boundaries.
Key takeaway: Socialization is shaped by broader cultural, institutional, and technological forces.
Learner Experiences and Reactions to Those Experiences
- Learners experience a mix of positive and negative emotions during training (e.g., excitement, anxiety, joy, shame).
- How learners respond to these emotions affects their sense of competence and belonging.
- If learners feel like they do not belong, they may:
- Become detached or cynical.
- Suppress parts of their identity.
- Withdraw from the profession altogether.
Key takeaway: Emotional experiences shape identity—medical education should support learners in processing these experiences.
Conclusion
- Professional identity formation is dynamic and evolving.
- The field of medicine must continuously re-examine its professional norms to ensure inclusivity.
- Medical educators should foster environments where learners can develop authentic professional identities without feeling pressured to conform to dominant cultural norms.
- The goal is to prepare future physicians who are competent, compassionate, and equipped to meet the diverse needs of society.
Key takeaway: A more inclusive approach to professional identity formation benefits both learners and the profession.
Final Thoughts
This paper challenges traditional views of professionalism in medicine and proposes a more inclusive, dynamic, and learner-centered approach. Instead of treating socialization as a one-size-fits-all process, it recognizes that professional identity is personal, evolving, and shaped by broader societal forces.
Would you like me to help summarize key takeaways for your own research or teaching purposes? 🚀
논문의 각 섹션에 대한 자세한 설명
제목: 존재(Being), 성장(Becoming), 소속감(Belonging): 의학에서의 전문직 정체성 형성의 재개념화
소개
지난 10년 동안 의학교육의 초점이 **전문직 행동(professionalism)과 역량(competencies)**에서 **전문직 정체성 형성(professional identity formation, PIF)**으로 이동해왔다. 즉, 단순히 전문직 규범을 따르는 것이 아니라, 의학 교육생들이 의사로서의 정체성을 형성하는 과정을 지원하는 방향으로 변화했다. 이 변화는 긍정적인 영향을 미쳤지만, 다음과 같은 예기치 않은 부정적 결과도 드러났다.
- 정체성 위협 및 배제(identity threat & exclusion): 기존의 PIF 모델은 소외된 집단의 경험을 충분히 반영하지 못하여 배제감을 유발할 수 있다.
- 지배적인 문화 규범의 과도한 강조: 의학 직업은 전통적으로 지배적인 문화 집단(예: 백인, 남성, 이성애자)의 가치관에 의해 형성되었으며, 이에 속하지 않는 사람들에게 동화(conformity)의 압력을 가할 수 있다.
저자들은 전문직 정체성 형성을 더 포괄적인 방식으로 재구성할 것을 제안하며, 다음을 강조한다.
- 사회화(socialization)는 수동적 과정이 아니라, 적극적이고 비판적인 참여가 필요하다.
- 학습자의 주체성(agency)을 강화하여, 그들이 전문직 정체성을 능동적으로 형성하도록 지원해야 한다.
- 소속감(belonging)과 배제(exclusion)가 전문직 자아(professional self)에 미치는 영향을 인식해야 한다.
이러한 접근 방식은 보다 다양한 전문직 정체성을 포용하는 교육 환경을 조성하면서도, 의학이 요구하는 높은 직업적 기준을 유지하는 데 도움을 줄 것이다.
전문직 정체성 형성 과정
이 섹션에서는 전문직 정체성이 의학 공동체에 사회화되는 과정에서 형성된다는 개념을 설명한다. 기존 모델이 권력 역학(power dynamics)을 충분히 반영하지 못했으며, 전문직 정체성 형성이 종종 지배적인 문화적 규범에 동화되는 과정으로 작용했음을 비판한다.
의학교육 프로그램 입학 시 기존 개인 및 전문직 정체성
- 의료 교육생들은 입학 전부터 **개인의 정체성(personal identity)**을 가지고 있으며, 이는 그들의 사회적 배경, 교육 경험, 가치관에 의해 형성된다.
- 이러한 사전 정체성은 그들이 의학 공동체에 어떻게 적응하고 참여하는지에 영향을 미친다.
- 정체성은 고정된 것이 아니라 시간이 지나면서 계속 변화한다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 의료 교육생들은 백지 상태로 입학하는 것이 아니며, 이미 형성된 정체성을 가지고 있다.
사회화 과정과 학습자의 반응
- 기존의 사회화 정의는 "개인이 특정 사회나 집단의 가치와 규범을 내면화하는 과정"이었다.
- 하지만 이 정의는 학습자가 단순히 규범을 수동적으로 받아들인다는 점에서 한계를 가진다.
- 저자들은 학습자들이 전문직 규범을 단순히 수용하는 것이 아니라, 비판적으로 검토하고, 필요하면 저항할 수도 있어야 한다고 주장한다.
- 사회화 과정에서 학습자들은 다음과 같은 다양한 반응을 보일 수 있다.
- 전문직 규범을 완전히 받아들임
- 일부 규범을 거부하거나 저항
- 자신의 가치관과 충돌하는 부분을 협상하고 조정
👉 핵심 메시지: 전문직 정체성 형성은 단순한 동화(conformity)가 아니라, 학습자가 적극적으로 참여하고 비판적으로 사고하는 과정이어야 한다.
개인 및 전문직 정체성의 발전
- 전문직 정체성은 정해진 형태로 완성되는 것이 아니라, 지속적으로 변화한다.
- 학습자는 의과대학 학생 → 인턴 → 레지던트 → 전문의로 성장하면서 새로운 전문직 정체성을 계속 형성한다.
- 하지만 전문직 정체성이 개인 정체성과 분리되면서, 일부 학습자들은 자신이 ‘가면(persona)’을 쓰고 있는 듯한 느낌을 받을 수 있다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 의료 교육은 학습자가 ‘진정한 자신(true self)’을 유지하면서도 전문직 정체성을 형성하도록 지원해야 한다.
실천 공동체(Communities of Practice)
- 의료 교육생들은 단 하나의 공동체에 속하는 것이 아니라, 여러 개의 실천 공동체(예: 의과대학, 병원, 학회, 연구 그룹 등)에 소속된다.
- 그러나 모든 학습자가 이 공동체에서 동일한 소속감을 느끼는 것은 아니다.
- 저자들은 기존의 단수형 "Community of Practice" 대신, "Communities of Practice"를 사용하여 다양한 전문직 환경을 반영하고 있다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 전문직 정체성은 다양한 공동체에서 형성되며, 소속감이 중요한 역할을 한다.
전문직 정체성 형성 과정의 요약
- 정체성 형성은 사회적 과정이며, 여러 요인에 의해 영향을 받는다.
- 학습자는 고유한 사전 정체성을 가지고 입학하며, 사회화 과정에서 이를 발전시킨다.
- 사회화는 단순한 적응이 아니라 비판적 사고와 적극적 개입이 필요하다.
- 개인 정체성과 전문직 정체성은 함께 진화한다.
- 소속감은 전문직 발전에 필수적인 요소이다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 새로운 모델은 학습자의 개별성을 존중하고, 다양한 정체성을 포용하는 방향으로 개선되었다.
사회화 과정에 영향을 미치는 요인
- 사회적·정치적 환경: 인종차별, 성차별 등의 이슈가 의학교육에 반영되어야 한다.
- 숨겨진 교육과정(hidden curriculum): 공식적인 교육과정 외에도, 암묵적인 가치와 태도가 정체성 형성에 영향을 미친다.
- 롤모델과 멘토링: 다양한 배경의 멘토가 부족할 경우, 특정 그룹의 학습자들이 소외될 수 있다.
- 소셜 미디어와 가상 공동체: 온라인 네트워크는 기회이자 위험 요소로 작용할 수 있다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 사회화 과정은 단순한 교육 과정이 아니라, 더 넓은 사회적·문화적 요인에 의해 영향을 받는다.
학습자의 경험과 정서적 반응
- 학습자는 훈련 과정에서 기쁨, 흥분, 불안, 수치심 등의 다양한 감정을 경험한다.
- 소속감을 느끼지 못하면 냉소적이거나 정체성을 억누르거나, 심지어 직업을 포기할 수도 있다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 의학교육은 학습자가 자신의 감정을 인식하고 반응하는 방식을 지원해야 한다.
결론
- 전문직 정체성 형성은 끊임없이 변화하는 과정이다.
- 의학은 더 포괄적인 전문직 규범을 정립해야 한다.
- 의료 교육은 학습자가 진정한 자신을 유지하면서도 유능하고 공감력 있는 의사로 성장하도록 지원해야 한다.
👉 핵심 메시지: 포용적이고 진정성 있는 전문직 정체성 형성이 환자 치료의 질을 향상시키는 데 기여할 것이다. 🚀
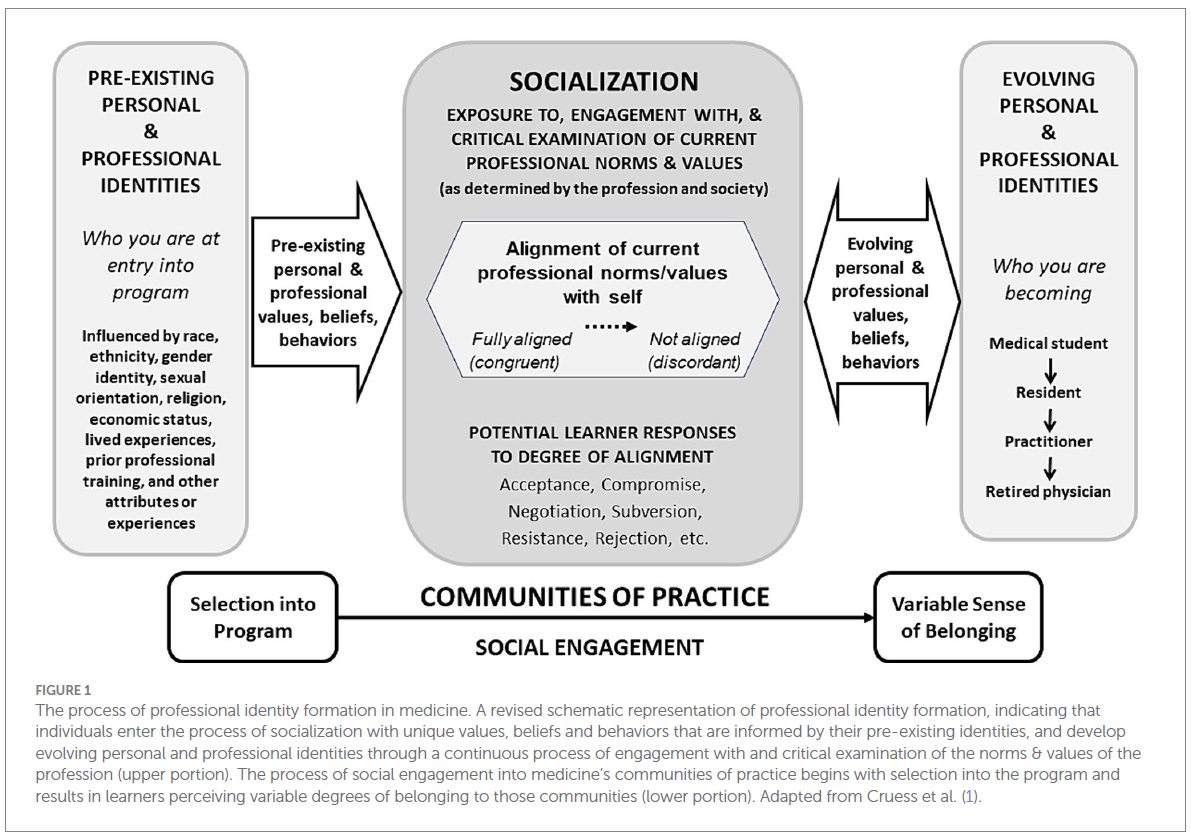
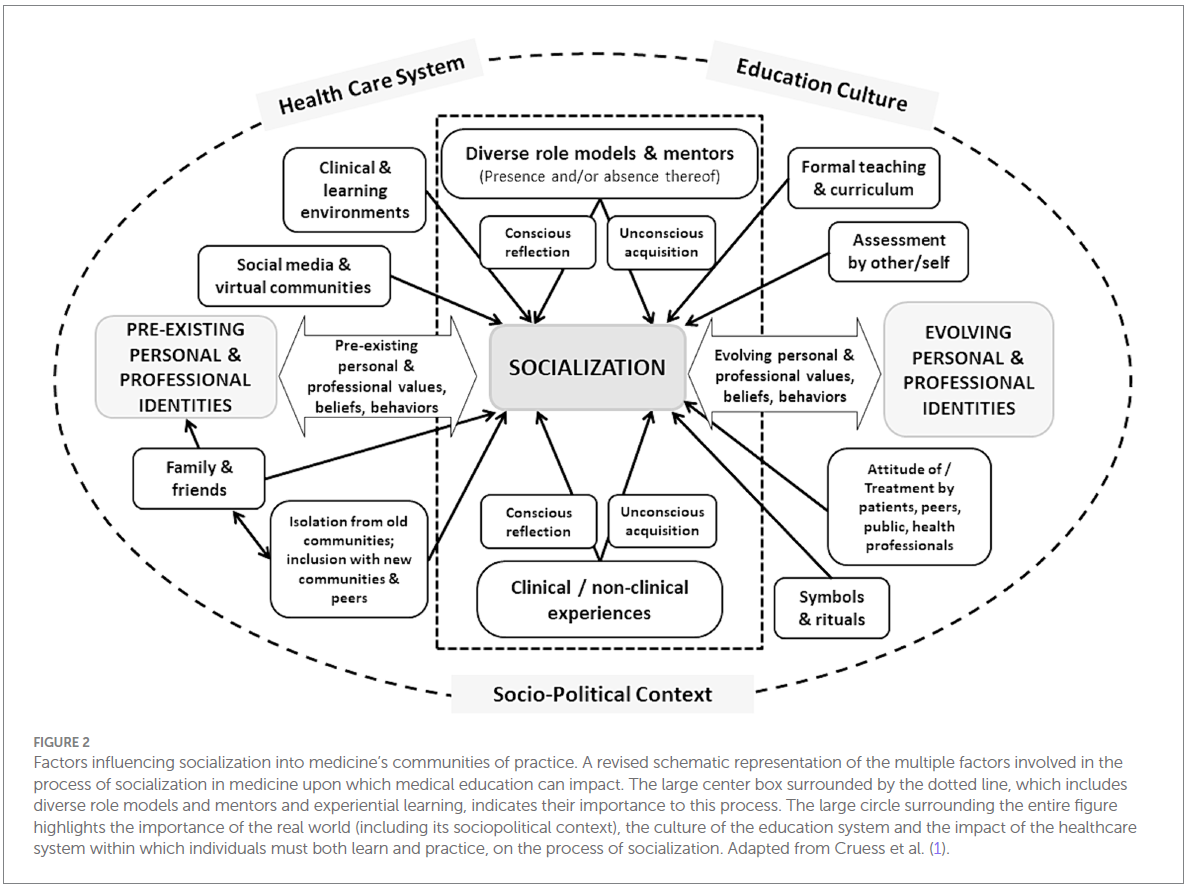
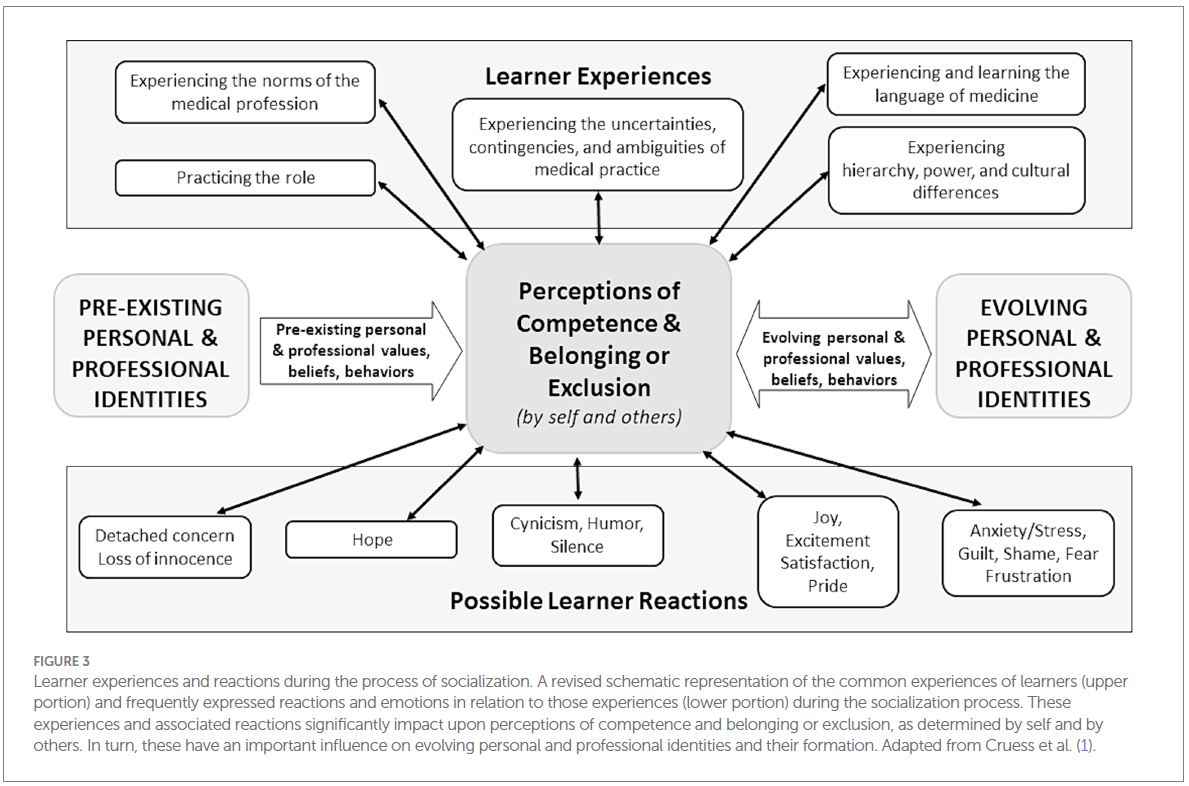
의학에서의 전문직 정체성 형성 과정 개념도 설명
이 개념도는 의학 교육생(learner)들이 사회화 과정에서 겪는 경험, 인식, 반응을 시각적으로 나타낸 것입니다.
📌 핵심 요소:
1️⃣ 학습자의 경험 (상단 영역)
의료 교육생들은 다양한 경험을 하면서 전문직 정체성을 형성하게 됩니다. 주요 경험들은 다음과 같습니다.
✔️ 의료 직업의 규범을 경험 (예: 의사로서 기대되는 행동과 가치 익히기)
✔️ 의사 역할 수행 (임상 실습 및 환자 치료 과정 경험)
✔️ 의료 실무에서의 불확실성, 변수, 모호함을 경험 (예측할 수 없는 상황과 복잡한 의학적 결정 경험)
✔️ 의학 용어와 언어 학습 (전문 용어 및 의사소통 방식 익히기)
✔️ 위계, 권력, 문화적 차이를 경험 (의료 시스템 내에서 권력 구조와 사회적 역할 차이 인식)
이러한 요소들은 학습자들이 전문직으로 성장하는 데 중요한 영향을 미칩니다.
2️⃣ 유능함(Competence), 소속감(Belonging) 또는 배제(Exclusion)의 인식 (중앙 영역)
의료 교육생들은 위의 경험을 바탕으로 자신을 어떻게 바라보는지, 그리고 타인이 자신을 어떻게 평가하는지에 대한 인식을 형성합니다.
🔹 나는 이 직업에서 유능한가? (Competence)
🔹 나는 이 공동체에 속한다고 느끼는가? (Belonging)
🔹 나는 소외감을 느끼는가? (Exclusion)
이러한 인식은 정체성 형성의 중요한 요소이며, 이후의 감정적 반응과 태도에 큰 영향을 줍니다.
3️⃣ 기존 및 변화하는 개인 및 전문직 정체성 (좌·우측 영역)
✔️ 학습자들은 각자 기존의 개인적·전문적 가치관과 신념을 가지고 의학 교육에 입학합니다.
✔️ 그러나 교육과 실습을 통해 새로운 경험을 하면서 전문직 정체성이 변화하고 발전하게 됩니다.
✔️ 즉, 의사의 정체성은 고정된 것이 아니라 지속적으로 형성되는 과정입니다.
4️⃣ 학습자의 다양한 반응 (하단 영역)
위의 경험과 인식에 따라 학습자들은 다양한 감정적 반응을 보일 수 있습니다.
✅ 긍정적 반응:
✔️ 희망(Hope) – 성장과 발전에 대한 기대감
✔️ 기쁨, 흥분, 만족, 자부심(Joy, Excitement, Satisfaction, Pride) – 소속감을 느끼고 보람을 경험
❌ 부정적 반응:
✔️ 냉소, 유머, 침묵(Cynicism, Humor, Silence) – 감정을 숨기거나 냉소적 태도로 반응
✔️ 떨어진 공감력, 순수함의 상실(Detached concern, Loss of innocence) – 감정적으로 거리 두기
✔️ 불안, 스트레스, 죄책감, 수치심, 두려움, 좌절(Anxiety, Stress, Guilt, Shame, Fear, Frustration) – 압박감과 소외감을 느끼며 고통받음
📢 결론 및 시사점
✔️ 이 모델은 전문직 정체성이 외부 경험과 내부 인식의 상호작용을 통해 형성됨을 보여줍니다.
✔️ 모든 학습자가 긍정적인 경험을 하는 것은 아니며, 배제되거나 소외감을 느낄 수도 있음을 강조합니다.
✔️ 따라서 의학교육자들은 학습자들이 도전에 적응하고 성장할 수 있도록 지원해야 하며, 소속감을 가질 수 있도록 환경을 조성할 필요가 있습니다.
의사가 되어가는 과정은 단순한 기술 습득이 아니라, 끊임없는 정체성 형성의 여정입니다. 🎯
궁금한 점이 있으시면 언제든 질문해주세요! 😊
Sternszus, R., Steinert, Y., Razack, S., Boudreau, J. D., Snell, L., & Cruess, R. L. (2024). Being, becoming, and belonging: reconceptualizing professional identity formation in medicine. Frontiers in Medicine, 11, 1438082.
'논문 읽기 (with ChatGPT)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 빠른 사고와 느린 사고를 넘어서: 변이이론적 임상추론 및 오류 모델이 교육, 평가, 그리고 연구에 미치는 영향 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
|---|---|
| 정보기반 근거이론 (Informed Grounded Theory) (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 근거기반실무 교육 개입의 보고 완전성: 체계적 검토 (0) | 2025.02.25 |
| 소아 응급실에서의 레지던트 민감 품질 지표: 감독자 신뢰도 및 환자 중증도·복잡성과의 관계 탐색 (0) | 2025.02.24 |
| 세분성이 중요하다: 자기 조절 학습을 측정하는 다양한 방법 비교 (0) | 2025.02.23 |